Farming has always been one of human history’s oldest and most fundamental occupations, but how we farm today vastly differs from how our ancestors did it. Modern technology has transformed the agricultural sector and led to the development of “smart agriculture,” which combines tried-and-true farming methods with cutting-edge smart agriculture technology to increase productivity and sustainability.
Precision agriculture, commonly called smart agriculture, uses advanced technology like IoT sensors, drones, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence to maximize yields and optimize resource utilization. This article examines the potential impact of climate smart agriculture on the agricultural sector.
The advantages of intelligent agriculture
Smart agriculture’s main objective is enhancing effectiveness, production, and profitability while limiting environmental impact. Farmers may learn about their crops, soil, and weather conditions using technology in real-time. Planning when to sow, irrigate, fertilize, and harvest their crops may increase yields while reducing expenditures.
In addition to promoting sustainability, smart agriculture uses less water, fertilizer, and pesticides. Instead of spreading these resources randomly throughout the entire field, this is accomplished by employing precise technology to distribute them to the required crops. Smart agriculture contributes to environmental protection and long-term sustainability by minimizing waste.
What IoT Sensors Do
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of connected things that can communicate with one another and other systems. IoT sensors are used in smart agriculture to track and gather information on a variety of variables, such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels. The growth and production of crops may then be optimized using this data.
For instance, based on the state of the soil, IoT sensors may choose the best time to grow crops. They are also used to track the development of crops and spot any symptoms of illness or stress. Farmers are thus able to take action before the issue worsens, which eventually results in improved yields and cheaper expenses.
Utilizing Drones
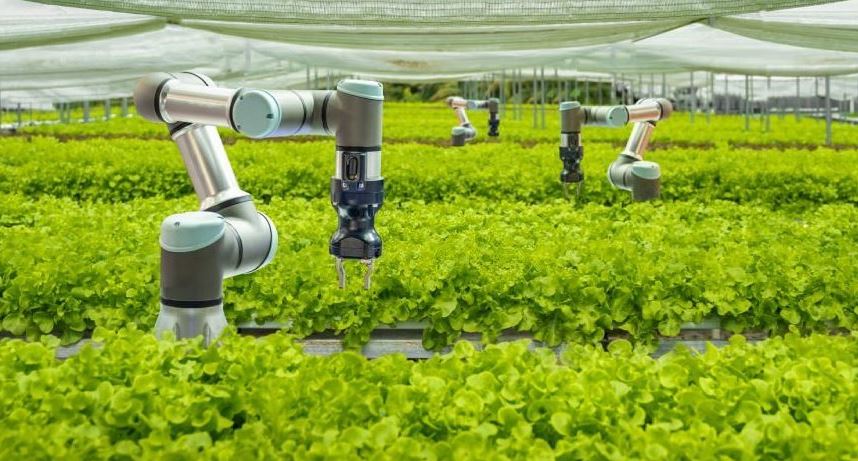
Drones are increasingly used in smart agriculture to provide farmers a bird’s eye view of their crops. This makes it possible for them to see problems—like stress or disease—quickly and take action before it’s too late.
Drones may map fields, and the 3D models they produce can be used to spot over or underused regions. This enables farmers to maximize harvests and use resources as efficiently as possible.
Data Analytics
Another essential element of intelligent agriculture is the utilization of big data analytics. Farmers can receive insights that would be hard to obtain through conventional techniques by evaluating and gathering vast data on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop development.
Climate smart agriculture, for instance, forecasts weather patterns and considers how they may affect crops. This enables farmers to take preventative actions to safeguard their crops and guarantee a successful harvest, such as adding more water or fertilizer.
Artificial Intelligence In Agriculture
Intelligent agriculture is likewise becoming increasingly dependent on artificial intelligence (AI). AI may use machine learning algorithms to examine data on crop growth, climate-smart farming methods, and soil quality to find trends and make forecasts.
For instance, based on preliminary weather data, AI can forecast the ideal crop growth time. Additionally, it may spot diseased or stressed regions in crops and suggest the best action to deal with the problem.
Precision agriculture, often known as smart agriculture, is a rapidly expanding field that uses technology to improve climate smart agriculture practices and increase productivity. As the world population approaches 9.7 billion by 2050, food needs will only increase. One strategy for satisfying this need while addressing issues with sustainability, effectiveness, and food security is smart agriculture.
Here are some ways that farming is being transformed by smart agriculture:
Precision farming includes accurately directing the administration of water, fertilizer, and pesticides to crops using technology such as sensors, drones, and GPS mapping. This has the effect of lowering input costs, raising yields, and enhancing environmental sustainability.
Data analytics: Farmers may choose when to sow, water, and harvest crops by gathering and evaluating weather patterns, soil moisture, and crop development. Higher crop yields, better resource management, and less waste can result. Automated farming uses robots and mechanical equipment to carry out operations, including planting, harvesting, and spraying crops. As a result, less physical work is required, and productivity rises.
Vertical Farming: Vertical farming involves growing crops vertically stacked layers using artificial lighting and controlled environments. This method allows for year-round crop production and efficient use of space, making it a promising smart agriculture solution for urban areas and regions with limited arable land.
IoT and Blockchain: Internet of Things (IoT) devices and blockchain technology can be used to track and verify every step of the farming process, from planting to distribution. This can improve transparency and traceability and ensure food safety and quality.
Conclusion
Technology will improve agricultural production, efficiency, and sustainability in intelligent agriculture. Global food security and agricultural sustainability will improve as these technologies evolve and become more available to farmers.